Phiat Review
Phiat
phiat.io
If your website is on the scam list and you think that you are not a scammer, contact us. After you provide us with all the proof that you are in Crypto World with good intentions, we will delist you. Usually, you get in this category because you are hiding your team, you have a bad reputation(you are tricking, deceiving, scamming people), and you haven't got a written project whitepaper or is a shitty one....
Their Official site text:
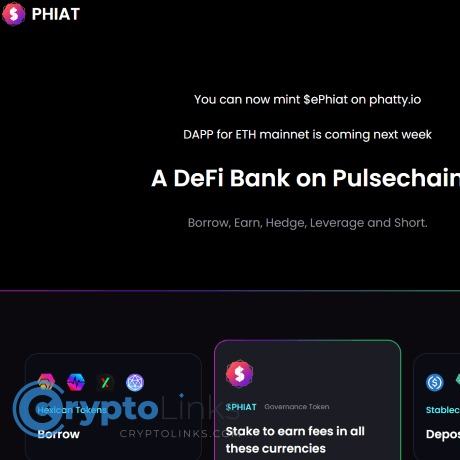
Welcome to Phiat
What is Phiat?
Phiat is a fork of AAVE V2 protocol. We assume you have reasonable knowledge about AAVE protocol and their tokenomics. Please check for more details.
Phiat is a decentralized protocol that gives individuals the option to either earn passive income by depositing funds or borrow money through a non-custodial market protocol for liquidity.
Why Phiat?
Built for RH Ecosystem participants and operating on multiple blockchains, Phiat operates independently of major governance or venture capitalist influence, instead opting for a revenue-sharing mechanism that benefits both token holders and liquidity providers. The platform is open-source, offering unrestricted access to all users and has undergone multiple security audits. With Phiat, you can borrow, earn, hedge, leverage, and short your favourite RH Ecosystem coins and more with ease.
It is indeed built to support free speech, even when it is hate speech directed against the Hex community, as we believe that giving them a secure environment to short our products is the best course of action.
How do I engage with Phiat Protocol?
Using the Phiat protocol is simple. All you need to do is provide your desired (supported) asset and quantity in a Metamask wallet. Upon successful provision, you'll earn passive income based on the demand for borrowing. Additionally, your assets will serve as collateral to secure loans. The interest earned from your provision compensates for the interest charged on borrowed funds.
What is the cost of interacting with Phiat protocol?
Using the protocol involves making transactions, which incurs transaction fees on the Ethereum blockchain based on network traffic and the complexity of the transaction.
Is there any risk?
It is an irrefutable fact that no platform can be deemed entirely devoid of risk. The Phiat protocol, like all others, is susceptible to two key risks:
The risk of an error or defect in the smart contract code.
The risk associated with the process of collateral liquidation.
To assuage these risks, the Phiat protocol has undergone a series of measures aimed at minimizing their impact, such as the adoption of battle-tested open-source code, comprehensive code audits, and ongoing risk management practices and maintenance.
Safety
Exercise extreme vigilance against the threat posed by phishing sites and fraudulent schemes purporting to be associated with Phiat. To safeguard your assets, it is imperative that you meticulously verify the legitimacy of all websites before transacting or providing any information. Ensure that you only utilize authorized Phiat platforms, thereby minimizing the risk of falling prey to unscrupulous actors.
PHIAT Protocol Tokenomics
$PHIAT is the platform's utility and governance token. The goal of the tokenomics is to incentivise the protocol's supporters and help long term growth of the community
Tokenomics
$PHIAT staking will be implemented as PHIAT protocol launches on mainnet.
The Interest paid by borrowers are classified as the platform fees
50% of the platform fees goes to lenders
50% of the platform fees (net fees) will be distributed to $PHIAT stakers:
All $PHIAT tokens are classified as stakable tokens, including:
Community share: 65%, fully circulating^.
Core team: 18%, locked for 12 months with a 10 months linear unlocking period. (please note locked team tokens can be staked and unstaked, but not sold or moved.)
Treasury: 10%, with target emission period of 24 months, given out to the community in the form of extra rewards.
OA and contributors: 7%, immediately unlocked, fully circulating
The $PHIAT token supply is distributed for the protocol to be owned fully decentralized
Rules of fee distribution:
If 100% of the tokens are staked, then 100% of the net fees will be distributed to the $phiat stakers, in the native currencies.
If x% of the tokens are not staked, then x% of the net fees will be distributed to the protocol treasury.
IMPORTANT: A 14-day cooldown period must be undergone prior to withdrawing your staked tokens. The unstaking process can be initiated by navigating to the staking tab, selecting 'unstake' and confirming with a single transaction. After initiating the cooldown, a 7-day withdrawal window will become available. Failure to withdraw during this period will necessitate repeating the cooldown process.
Rewards claim: You may access and retrieve your earned rewards anytime through the staking section by clicking the "Claim" button. The tokens obtained from the reward will promptly be transferred to your linked wallet once the transaction is validated.
Treasury operations will be openly discussed, transparently disclosed and potentially encoded in smart contracts.
^ Both Community and Contributors will have all their allocated tokens available before/from platform launch day, and 100% freely tradable.
ePhiat FAQ
Why ePhiat
The Phiat protocol has altered its original plan of being exclusive to PulseChain and has decided to launch on Ethereum to allow for a multi-chain approach. Participants in the initial $PHIAT phase will receive both $ePHIAT and $PHIAT on the PulseChain mainnet. Those who joined the Early-Bird Phamous Phase will receive a bonus in the form of $ePHIAT, but will not receive $PHIAT on PulseChain. This ensures that the original $PHIAT participants are not diluted and remain unchanged. The staking process will remain the same for both platforms, as previously outlined.
Like $PHIAT, the supply distribution of $ePHIAT is exceedingly decentralized
PulseChain fork:
We will guide the community through the procedures related to the upcoming Pulse fork. Once the PulseChain mainnet is near and we have a clearer understanding, it's crucial to ensure the safety of user funds. To achieve this, we will communicate effectively and efficiently with the community throughout the process. To prevent exploitation or gaming during the Pulse launch, several preventive measures will be put in place.
$ePHIAT Token Copy:
Upon the realization of the PulseChain snapshot, a replica of the token $ePHIAT will be created. However, a freshly minted token possessing a new contract shall be put into circulation and recognized as the legitimate and economically valuable token, which will be just $PHIAT. Thus, depriving the replicated token, copied $ePHIAT, of any inherent worth. It is crucial to be vigilant during this period and active in the Telegram to guarantee that you are interacting with the correct address.
Depositing
How do I deposit?
To make a deposit, go to the "Deposit" section and select the asset you wish to deposit. Choose the amount you want to deposit and initiate the transaction. Once it is confirmed, your deposit will be recorded and you will start earning interest.
*Note that the first deposit of a specific asset will require an additional approval step.
How much will I earn?
Phiat depositors receive continuous earnings that evolve with market conditions.Every asset has its unique market of supply and demand, and its Annual Percentage Yield (APY) fluctuates over time.
Is there a minimum or maximum amount to deposit?
There are no restrictions on the amount one may deposit. However, it must be taken into account that when depositing notably small amounts, the cost of the transaction process may outweigh the expected return. Hence, it is advisable to proceed with caution and carefully consider this factor when depositing excessively modest sums.
Can I opt-out my asset from being used as a collateral?
Yes, you have the option to exclude certain assets from being employed as collateral after making a deposit. This option can be accessed in the "Deposit" section of your account dashboard, where you may toggle the "Collateral" switch for the specific asset you wish to exempt from collateral utilization.*It is possible to withdrawl one's assets, provided that said assets are not being employed as collateral for an ongoing loan and the act of withdrawal does not result in the trigger of a liquidation event in regards to said loans.
How do I withdraw?
To initiate a withdrawal, access the "Withdraw" section within the dashboard and select the amount to be withdrawn. Proceed with the submission of the transaction.
Why is my coin not listed?
The absence of certain tokens might spark some disappointment. This may stem from inadequate internal evaluation, which considers elements such as liquidity, the asset's lifespan, and adherence to internal standards. Our aspiration is to present only the most impeccable assets and refrain from those that are ephemeral in nature. We will persistently strive to maintain a harmonious balance between our internal standards and the demands of the community ensuring that both the protocol and users are safeguarded from undue risk. It is crucial to keep in mind that one should not harbor any expectations regarding the introduction of new tokens.
Borrowing
Why borrow instead of selling my assets?
Selling assets involves giving up ownership of that asset and may result in missing out on potential gains or triggering a taxable event. On the other hand, the utilization of borrowing affords an individual the ability to acquire liquidity or operational capital without being compelled to part with their assets. This methodology is frequently adopted by individuals striving to accommodate unforeseen outlays, amplify their holdings, or venture into new investment opportunities.
How do I borrow?
To borrow, you first need to provide an asset as collateral. Then, navigate to the "Borrow" section and select the asset you wish to obtain a loan for. Determine the necessary amount based on the available collateral that you have deposited.
How much can I borrow?
The amount you are eligible to borrow is contingent upon the value of your collateral deposit and the existing liquidity.If the liquidity is insufficient or your "health factor" does not meet the criteria, borrowing an asset may not be possible.
Which asset am I responsible for repaying?
Repayment of your loan is made in the same asset in which it was borrowed. For instance, if 1 ETH is borrowed, 1 ETH plus accumulated interest must be repaid. If a loan is desired to be settled based on the USD value, any of the stable coins supported in the protocol may be borrowed.
How much would I pay in interest?
The rate of interest payable for the acquisition of assets through borrowing is contingent upon the borrowing rate, which is derived from the equilibrium between supply and demand for the asset in question. The borrowing rate can be consulted at any moment within the "Borrowings" section of one's dashboard.
What is the health factor?
The Health Factor serves as a numerical indicator of the stability of the deposited assets in relation to the borrowed assets and their intrinsic value. The greater the value of the Health Factor, the more secure the funds are from the likelihood of liquidation. Upon reaching a Health Factor of 1, the deposit will trigger automatic liquidation. If the Health Factor falls below 1, the deposit is susceptible to liquidation. In the event of a Health Factor of 2, the ratio of collateral to borrowed funds may diminish by half (1 out of 2). The Health Factor is calculated by evaluating the liquidation threshold of the collateral against the value of the borrowed assets.
What happens when my health factor is reduced?
The Health Factor is a variable metric, subject to alterations as a result of fluctuations in the value of the deposited underlying assets. An increase in the Health Factor improves the safety of the borrow position, making the occurrence of liquidation less probable. Conversely, a decrease in the value of the collateralized assets in relation to the borrowed assets will result in a corresponding decrease in the Health Factor, elevating the risk of liquidation.
When do I need to pay back the loan?
The repayment of the loan is not subject to a fixed timeline and may be prolonged indefinitely as long as the stability of the borrow position is sustained. However, with the passage of time and an accrual of interest, the Health Factor may also decline, thereby elevating the risk of liquidation of the collateralized assets.
Avoiding liquidation
To prevent the Health Factor from decreasing to the extent of triggering liquidation, you may choose to either repay the loan or make additional deposits to improve the Health Factor. Of the two available alternatives, repaying the loan would result in a more substantial enhancement of the Health Factor. It is important to ensure that you possess a thorough understanding of the inherent risks involved and possess an adequate knowledge of the utilization of these tools prior to proceeding.
Liquidation & Flash Loans
Can I participate in the liquidations ecosystem?
Processing liquidations are open to anyone, but competition among liquidators can be intense. To gain an advantage, they often create their own strategies and tools such as bots to quickly liquidate loans and earn the bonus, requiring a strong understanding of the process and development skills
What is a Flash Loan?
A Flash Loan offers the opportunity to obtain any quantity of assets without providing collateral, as long as the protocol's liquidity is reinstated within a solitary block transaction. The execution of a Flash Loan requires the formulation of a contract that initiates the loan request. The contract must then execute the prescribed procedures and repay the loan, along with all associated interest and fees, in a single contract transaction.
Can anyone do a flash loan?
Flash Loans are technically accessible to all, however they are specifically tailored towards individuals possessing prior knowledge and technical proficiency, specifically in the realm of coding and smart contract development. Thus, only those possessing an adequate level of understanding in these areas are capable of successfully participating in a Flash Loan
Token Minting Terms
$ePHIAT & $PHIAT
This document serves as a disclaimer and terms for the act of minting the tokens. Before participating in the token minting process, please take the time to read and understand the following important points. "Tokens" mentioned below would be referring to $ePhiat on ETH mainnet and $Phiat on PulseChain mainnet.
No Public or Private Sale
It is important to note that there is no public or private sale of the tokens ever. The tokens are mintable by those community members in recognition of their free speech via past on-chain activities. If you are not eligible to participate in the minting process, please do not attempt to do so.
Token Value
Furthermore, it is important to note that the tokens have no inherent value. Token minting is not an investment opportunity. Instead, the minting process serves as a means to create a digital asset that can be used within a specific ecosystem. Phiat protocol is a fork of Aave v2 and was completed in early 2022. It has been live & fully functioning on PulseChain testnet v2 since then. ePhiat are the ETH version of the protocol. There should be no expectation of any economic return or other benefits by minting the tokens. Any further token price move and staking activities would be pure community & market activities.
Restrictions on Participation
Please note that United States citizens and OFAC-sanctioned citizens are not expected to participate in token minting. The laws and regulations surrounding digital assets in the United States are complex and constantly evolving. As such, we cannot guarantee the legality or compliance of minting this token for individuals residing within the United States. It is your responsibility to ensure that you are eligible to participate in the minting process.
We have also conducted a crosschecking against OFAC sanction address list & some community maintained blacklist and have found none of our community addresses is included. We reserve the right to do this regularly on an ongoing basis.
Decentralization
The protocol and token contracts are fully decentralized on blockchain(s), and front-end pages are hosted on peer-to-peer IPFS network. The tokens supply are also exceedingly decentralized for both $PHIAT and $ePhhiat. No one is controlling protocol back-end, front-end or majority of any token supply. As a result, the community members who participate in the minting process bear the sole responsibility for the outcomes of their actions.
Phiat Team Responsibility
Finally, the Phiat team is only responsible for software development and not any financial liability. The team will not be held liable for any issues that arise due to community members' actions. If you choose to participate in the minting process, you do so at your own risk.
Thank you for taking the time to read this document. We highly recommend that all potential token minters seek legal counsel before participating in the minting process.
PH Glossary
#
51% Attack: An attack on blockchain by a group of miners controlling more than 50% of network hash rate
2x: on a double, on a double, on a double…
A
All-Time-High (ATH): The highest point (in price, in market capitalization) that a cryptocurrency has been in history.
All-Time-Low (ATL): The lowest point (in price, in market capitalization) that a cryptocurrency has been in history.
Arbitrage: A strategy where investors buy a currency in a market and sell it at a higher price in another market to gain profit.
Ask Price: The lowest price a seller is willing to accept on their sell order.
APY: Annual Percentage Yield, which is the yield/interest after a year, which includes compounding interest. Note that this is different from Annual Percentage Rate (APR), which does not take into account compounding effects.
B
Bagholder: A person who is holding a large quantity of cryptocurrency which is declining in value or becoming worthless
Basis Point: Unit of measurement used to quantify the change between two percentages
Bear Market: A market that is in a downward trend, with prices falling and investors becoming bearish.
Bearish: A term used to indicate negative sentiment towards the market or an asset, where investors believe that there will be downward price movement.
Bid Price: Value of buyers offer for a asset
Block: In the context of blockchain, block refers to the collection of transactional data or information that are bundled together in a predetermined size.
Block Confirmation: Refers to the number of confirmation a particular block has. Each block ahead of the referenced block adds one block confirmation to it.
Block Explorer: Applications or websites which display information such as status of transactions or data contained in a block of a given public blockchain network.
Block Height: A number that is used to indicate the position of a particular block within a blockchain.
Block Reward: One of the mechanisms built into a blockchain to incentivize validators.
Blockchain: A decentralized, distributed database that stores a record of all transactions that have occurred on a network.
Bloodbath: In the context of trading, the term bloodbath is commonly used to describe a market which is on a downtrend with many assets suffering from value depreciation.
Borrow: The act of obtaining digital assets from a lending platform and using them as collateral to trade or speculate on price movements. The borrower must pay interest on the borrowed assets and is responsible for returning them in full to the lending platform at the end of the loan period
Breakout: When the price of an asset moves outside of a defined range or pattern, typically by breaking out of a support or resistance area
Bull Market: A market that is in an upward trend, with prices rising and investors becoming bullish.
Bullish: A term used to indicate positive sentiment towards the market or an asset, where investors believe that there will be upward price movement.
Backwardation: a market condition where the future price of an asset is lower than its spot price
Burned Tokens: Tokens which have been sent to addresses whose private keys are not known, effectively becoming unusable.
Buy Wall: An anomalously large buy order(s) at a single price point that reflects as a "wall" in the order book.
Buy/Sell Tax: On-chain buy or sell tax rate where a percentage of the tokens bought/sold will be transferred to a set address.
Buy the F***in Dip (BTFD): An encouraging rally by asset/cryptocurrency supporters to buy during a price decline.
C
Centralized: A type of organization or network in which a small number of actors have control over the entire system.
Central Ledger: A central data repository maintained by a company or bank.
Circulating Supply: An estimated amount of coins or tokens that are currently not locked and available for public transactions.
Cold Storage: A method of storing cryptocurrency offline, in order to reduce the risk of it being stolen by hackers. This can include the use of hardware wallets or paper wallets.
Cold Wallet: A type of cryptocurrency wallet that is offline and requires physical access to certain devices, such as hardware wallets or paper wallets.
Consensus: The agreement among participants in a blockchain system on the content of the next block to be added to the blockchain.
Crypto Bubble: A speculation that the price of cryptocurrencies will rise to extremely high levels before collapsing.
Cryptocurrency: A digital currency that uses cryptographic protocols to record ownership and prevent counterfeiting.
Capitulation: A period of strong selling activity, where investors give up their positions and sell as quickly as possible
Censorship-resistance: The property of a cryptocurrency network that prevents any entity from altering transactions on it
Custody: Protective care or guardianship of an asset.
Confirmation Time: The time elapsed when a transaction is submitted to the network and the time it is recorded into a confirmed block.
Confluence: When multiple investment methods, technical indicators, or trading signals are combined to form a more reliable strategy.
Consumer Price Index (CPI): A Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure used to track the effects of inflation over a period of time.
Crypto Winter: The term crypto winter refers to an extended period of declining or stagnant prices and negative sentiment in the cryptocurrency market.
Cryptocurrency: A digital currency that is secured by cryptography to work as a medium of exchange within a peer-to-peer (P2P) economic system.
D
Dead Cat Bounce: A temporary recovery in the price of an asset after a prolonged decline, which is not indicative of a market turnaround.
Decentralized: A system that does not have a central point of failure or organization, and is not controlled by a single authority.
Decentralized Applications (dApps): Applications that run on decentralized, peer-to-peer networks such as Ethereum.
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO): Open source and decentralized systems that do not require centralized operators or controllers.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): A movement focused on building decentralized financial applications that are not controlled by a central authority and are censorship-resistant.
Decentralized Exchange (DEX): An exchange that does not require users to deposit funds to start trading and does not hold the funds for the user. Instead, users trade directly from their own wallets.
Delisting: The removal of an asset from an exchange, either as a request from the project team or as a decision made by the exchange.
Delta Neutral: Delta neutral is the construction of positions that do not react to small changes in the price of the underlying asset. No matter if the underlying asset goes up or down, the position maintains its value and neither increases or decreases in price.
Diamond Hands: A term used to describe holding a financial asset and not selling it, regardless of its volatility.
Divergence: When the market price of an asset and a technical indicator (such as RSI, Volume, MACD) move in opposite directions.
Diversification: The allocation of funds across different types of assets and jurisdictions in order to reduce overall risk.
Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA): A strategy of investing fixed dollar amounts over regular intervals of time, regardless of the price of the asset.
Degen: Cryptocurrency trading without proper research and due diligence, often seen as akin to gambling.
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (dPOS): A consensus mechanism in which selected members of a network are voted upon as delegates to validate transactions and produce blocks on a blockchain.
Derivatives: Financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset or index, such as futures or options.
Derivatives Market: A market for derivatives, which are financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset.
Difficulty: A measure of how difficult it is to correctly guess the solution to a new block in a blockchain.
Distributed Ledger: A ledger whose data is stored and synced across a network of nodes.
Dominance: Typically refers to the market capitalization dominance of Bitcoin.
Double Spending: The act of spending digital currencies twice, which is often carried out by unscrupulous actors on cryptocurrency exchanges.
Do Your Own Research (DYOR): Advice for investors to conduct their own research on the coins they are considering investing in.
Dump: A term used to describe a downward movement in the market, or the act of selling an individual's holdings.
Dusting Attack: A form of malicious activity in which hackers and scammers attempt to compromise the privacy of cryptocurrency users by sending small amounts of money to their wallets.
E
Emission: The rate at which new coins are released according to predetermined protocols.
Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH): An economic theory stating financial markets reflect all available information on the price of assets at any time.
ERC-20: A standard for creating exchangeable, fungible tokens on the Ethereum blockchain.
ERC-721: A standard for creating exchangeable, non-fungible tokens on the Ethereum blockchain.
Ethereum: A decentralized computing platform and cryptocurrency that enables the creation of smart contracts.
Ethereum Name Service (ENS): A service that allows Ethereum users to find websites or send and receive funds using simple names.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): The environment in which all smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain are executed.
F
Faucet: A site or app where users can go to receive small rewards over time.
Fauxican: Someone who is pretending to be a Hexican
Falling Knife: The act of purchasing an asset while it is rapidly declining in price, with the expectation that it will bounce back.
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): A feeling of anxiety or regret over potentially missing out on a profitable investment opportunity. Often used to describe investors' fear of missing out on the opportunity to buy cryptocurrencies that may become profitable.
Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt (FUD): A strategy that involves spreading false information in order to discourage people from buying a particular cryptocurrency.
Fake Out: A situation where a trader enters a position based on an anticipated price movement that quickly reverses or does not occur.
Fiat: A currency that has been established as a valid form of money, typically supported by a government regulation that declares it to be legal tender.
Finality: The assurance that completed (cryptocurrency) transactions cannot be altered, reversed, or canceled.
First-Mover Advantage (FMA): The competitive advantage of the first project to introduce a service or product into a new and unexplored market or industry.
Fiscal Policy: The policies that involve the government adjusting tax rates and how public funds are collected and used.
Flippening: One cryptocurrency overtaking another.
Furu: Usually a charlatan who is attempting to be an expert or highly acknowledged in a certain field, in this case cryptocurrency
Frontrun: The act of intercepting a large buy order on an automated market maker (AMM) in order to purchase the assets and resell them back to the buyer before the order is executed on the blockchain.
Fully Diluted Valuation (FDV): The market capitalization if the maximum supply of a coin is in circulation. Calculated by multiplying the current price by the max supply.
Fungibility: The property of an asset in which its individual units are indistinguishable from each other in terms of value and functionality.
Futures Contract: A standardized version of a forward contract, used as a legal agreement to buy or sell an asset in the future at an agreed upon price and date.
Full Node: A computer that verifies the rules built into the protocols of a particular cryptocurrency.
Fundamental Analysis (FA): The evaluation of an asset based on its underlying characteristics and traits, in an effort to determine its intrinsic value.
FOMC: Federal Open Market Committee
Forced Liquidation: The forced closure of a trader's leveraged position due to it not meeting the necessary margin requirements.
G
Goblin Town: A term used to describe the market's persistent downtrend, synonymous with "bear market".
Gas: A unit of measurement of the computational effort in conducting transactions or smart contracts on Ethereum blockchain.
Gas Limit: A term refers to the maximum amount of units of gas user's willingness to spend on a transaction on Ethereum blockchain.
Gas Price: A term refers to the amount of price a user is willing to pay for a transaction on Ethereum blockchain.
Gwei: A unit of Ethereum's native currency, ether, used to pay for transactions on the Ethereum network.
H
Halving: When the block reward of a crypto asset, such as bitcoin, drops to one-half of what it was before; this is used to create a decaying rate of issuance to arrive at an eventual finite supply of a crypto asset.
Hash Rate: The speed at which a computer or mining hardware is able to
Hedge: Hedging is a risk management strategy in place to offset losses in investments by taking an opposite position in a related asset
Helicopter money: Term used for a large sum of new money that is printed
Health factor: Represents the ratio between total collateral multiplied by the liquidation threshold, and the borrowed principal.
Honeypot: The form of a fake wallet or a phishing website that appears to be a legitimate exchange or wallet service, but is actually designed to steal users' private keys, passwords, or other sensitive information.
HODL: A typo of 'Hold' originating from bitcointalk that has also been retrofitted to be an acronym for Hold on for Dear Life - to maintain ownership of coins and not sell.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT): A type of algorithmic trading that involves the execution of a large number of orders in fractions of a second.
I
Immutability: The inability to change or be changed. One of the core features behind Bitcoin and blockchain technology.
Index: A financial instrument used to track the price value of a given asset or basket of assets.
Interoperability: A concept of allowing blockchains to be compatible with each other and build upon each other's features and use-cases.
Isolated Margin: The margin balance allocated to a position. Traders can manage risk by restricting the amount allocated to each position.
Issuance: The generation of a new cryptocurrency which occurs in a variety of different ways, depending on parameters specified by the creators.
J
Judas candle: A red bearish candle followed by a long bullish reversal candle.
K
Know Your Customer (KYC): A standard procedure in the finance industry which allows companies to identify their customer and comply with KYC and AML laws
L
Latency: The time between submitting a transaction to a network and the first confirmation of acceptance by the network.
Ledger: A record of all transactions that have occurred on a network. In the context of cryptocurrency, a ledger can refer to either a physical book that records transactions, or a digital record of transactions stored on a network
Leverage: Multiply your exposure to a financial asset without additional investment capital
Listing: The addition of an asset to an exchange either as a request from the project team or as a decision made by the exchange.
Liquidation Bonus: The bonus received by liquidators to incentivise the purchase of specific collateral that has a health factor below 1. The Liquidation Bonus is specified per collateral and expressed in percentage points.
Liquidity: The ability to sell or buy any given asset without causing significant fluctuations in the market price for that asset.
M
Maintenance margin: Amount that must be avalable in order to keep a margin position open
Market capitalization (market cap): In Crypto, market cap is measured by multiplication of the circulating supply of tokens or currency and its current price.
Market Maker: A participant of the market who creates buy and sell orders.
Market Order / Market Buy / Market Sell: A market order is a buy or sell order of stocks or cryptocurrency at the best price available in the current market as soon as possible.
Market Taker: A participant of the market who buys and sells from currently existing orders.
Margin Call: A margin call takes place when an investor's margin account falls below the required amount to stay afloat.
Margin Trading: It is a way of investing by borrowing money from a broker (or in crypto, an exchange or platform) to trade.
Metaverse: The Metaverse is a virtual space where users are able to interact with each other in a computer generated environment.
Moritz: He is known for his trading strategies (though he never trades), philanthropy and incredible humility. Moritz Is the single largest holder of WISE. Moritz is usually at least 1 step ahead of RH. Never go full Moritz
Money Printer Go Brrr: A meme made to describe the US Federal Reserve printing an excessive amount of money to support the traditional financial market to avert the stock market crash in 2020
Moon: "Moon" or "To the moon" is a crypto slang that describes an exclamation when the cryptocurrencies prices are rising, and when it hits the peak, the coin is said to be "mooning".
Multisignal (multi-signature): They are wallets that require more than one key for transactions to be authorized.
O
Order book: A list of orders for a particular asset that are being managed by an exchange.
Off-chain: Transactions occurring outside the blockchain and executed instantly.
Open/Close: The price at which a cryptocurrency opens at a specific time period (e.g. start of the day) and the price at which a cryptocurrency closes at a specific time period (e.g. end of the day).
Oracles: Services that verify real-world data and provide it to blockchains or smart contracts.
Over The Counter (OTC): The process of trading cryptocurrencies outside of exchanges and directly between two parties.
P
Passive Management: An investing strategy that tracks an existing economic index rather than relying on active market exposure.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P): A connection between two or more computers that share workload or resources without relying on a centralized server.
Pegged Currency: A currency whose price is designed to remain the same as a designated asset (e.g. 1 USDC is pegged to 1 USD). Also known as a stablecoin.
Perpetual contract: A perpetual contract is a crypto futures contract without an expiry date thus can be held indefintley
Phishing: A malicious attack in which a bad actor tries to obtain a user's credentials in order to gain unauthorized access to their account.
PRC-20: A standard for creating exchangeable, fungible tokens on the Pulse blockchain.
Ponzi Scheme: A scam in which new investors' funds are used to pay returns promised to previous investors. Do not invest in these.
Price Action: The price movements of a financial asset over time. When plotted on a chart, it can be used by traders to identify trade setups.
Private Sale: An early stage investment round for strategic investors with a large amount of investible funds.
Proof of Stake (PoS): A consensus algorithm that assigns block validation based on the coins or tokens locked in by the validator.
Proof of Work (PoW): A consensus algorithm in which a block is validated through mathematical hashing.
Portfolio: A collection of all your current cryptocurrency holdings
Phatty: An aggregated read-only wallet that helps you track your portfolio cross-chain.
Pump and Dump Scheme: A market manipulation method of driving up the price of an asset before profiting by driving it back down.
R
Real Market Player: Someone who is just a real market player
Rekt: A slang term for "wrecked," typically used to describe bad trades that result in losses.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): A popular technical indicator used to analyze financial markets by charting the current and historical closing prices to evaluate overbought/oversold conditions. RSI oscillates between 0 and 100, with values less than 30 indicating oversold conditions and values greater than 70 indicating overbought conditions.
Revenue Sharing: The distribution of revenue generated to stakeholders or contributories
Risk Management: Process of identifying potential risks in your investments
ROI: Short for "Return on Investment," the ratio between the net profit and cost of investing.
Rug Pull: The sudden removal of liquidity, which often leads to asset prices crashing due to a lack of liquidity to absorb buy/sell orders.
Resistance: A term in technical analysis (TA) used to describe a price that is increasing and finds resistance, typically compared with previous highs.
Roadmap: A business planning technique that outlines the short- and long-term goals of a company within a flexible estimated timeline.
Revenue Sharing: The distribution of revenue generated to stakeholders or contributories
Richard Heart: The founder of Hex.com, a cryptocurrency ‘the world's first high-interest blockchain certificate of deposit’ and PulseChain, a proof-of-stake (PoS) fork of Ethereum. Raised $27m to charity to save your life. Has the world's largest diamond, multiple sports cars and mult-million watch collection. Called the top on the day. Its been in profit every single day expect one day when we had that judas candle
S
SAFU: A cryptocurrency term for "safe”.
Scalp: Opening a position with the intent to close a profit in a short timeframe
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): An independent governmental agency responsible for regulating securities markets.
Security Audit: A systematic analysis to evaluate how secure a system, smart contract, or blockchain is against attacks or technical failures.
Sell Wall: A very large limit sell order or an accumulation of sell orders at the same price level on an order book for an asset.
Sentiment: The overall attitude of a community towards a cryptocurrency or within investors towards a certain financial market.
Sharpe Ratio: A ratio created in 1966 that investors and economists use to assess the potential return on investment (ROI).
Smart Contract: Automated contracts that trigger certain actions when predetermined conditions are met. They work like "If...then" conditions, such as requiring condition C to be met before money can be transferred from A to B.
Snapshot: The ability to record the state of a blockchain ledger, storage device, or computer system at a specific point in time.
Spread: Difference in price between the buy(bid) and sell (ask)
Spot: Spot price is the current value of an underlying asset
Stablecoin: A type of cryptocurrency that is designed to maintain a stable value, rather than experiencing significant price changes.
Staking: In crypto, staking is the incentive model of locking up crypto holdings in order to obtain rewards or earn interest.
Staking Pool: A pool where stakeholders combine their staking power to increase their chance of successfully validating a new block.
Store of Value: A commodity, asset, or currency that can be saved, retrieved, and exchanged at a future date without suffering depreciation.
Support: In technical analysis (TA), support refers to a price level at which demand for an asset is thought to be strong enough to prevent the price from declining further.
Stable rate: A loan with a stable rate behaves like a fixed rate loan in the short term, but the rates can be rebalanced following sudden market changes in the medium/long term.
T
Technical analysis: The study of historical price and volume data in order to identify patterns and trends that can be used to make investment decisions.
aker: Someone who places an order that is immediately matched with an existing order on the order book.
Tank: A strong negative financial performance of a particular asset, adopted from traditional financial markets.
Ticker: The trading symbol or shortened name (usually in capital letters) that refers to a coin on a trading platform. For example: BNB
Token: Digital units issued on a blockchain that can hold value or be redeemed for assets.
Token Lockup: The time during which tokens or coins are not allowed to be transferred or traded.
T-Shares:T-Shares means trillion shares. A user’s HEX and stake days are ultimately converted to shares. When calculating a user’s portion of day’s inflation + penalty payments, they receive an amount equal to their stake’s Shares / Total shares in existence on that day.
Total Supply: The number of coins or tokens that currently exist and are either in circulation or locked in some way.
Transaction ID (TXID): A unique string of characters that labels each transaction on the blockchain.
Transactions Per Second (TPS): The number of transactions that a blockchain network is capable of processing per second.
Trustless: A system in which no single entity has authority and consensus is achieved between participants who do not need to trust each other.
Token Burn: An event in which tokens are permanently and verifiably removed from circulation.
Total Value Locked (TVL): The number of assets that are currently staked in a protocol or the total quantity of underlying funds that a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol has secured.
Trading Volume: The amount of cryptocurrency that has been traded in the past 24 hours.
Transaction Fee: A payment to the network for recording a transaction on the blockchain.
Testnet: A staging area for experimenting with new blockchain features, short for "test network."
U
Utility Token: cryptocurrency tokens with specific utilities on a network besides being used as medium of exchange and investment vehicle.
V
Volatility: How quickly and how much the price of an asset changes. Calculated in terms of standard deviations in the annual return of an asset over a set period of time
Volume: A measurement of the number of individual units of an asset that changed hands in a market during a given time.
Validator: A block-signing participant of a Proof of Stake blockchain network, who have significant tokens staked on the network.
W
Wallet: A software program that stores a user's private and public keys, and allows them to send and receive cryptocurrency.
Wen Lambo: An expression used by investors to ask when the value of their investment could buy them a Lamborghini
Wen Moon: An expression used by investors to ask when the price of a coin would hit a peak
Whitelist: A list of allowed or trusted individuals, computer programs, or cryptocurrency addresses in relation to a service or event.
Wick: A line found on a candlestick chart that indicates where the price of an asset is fluctuating in relation to its opening and closing prices.
Win Rate: In financial markets, the win rate (or win ratio) is a metric that indicates how profitable a trader might be.
Wrapped Ether (WETH): An ERC-20 token representing Ether at a 1:1 ratio. It allows users to trade ETH for ERC-20 tokens on decentralized platforms.
Y
Yield: interest earned from an investment through staking or providing liqudity
Yield farming: The act of using liquidity in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to earn a return on one's capital, typically through providing liquidity
YTD: Acronym for Year-to-date
Z
Zero-knowledge proof: A method of proving that something is true without revealing any additional information about it. In the context of cryptocurrency, a zero-knowledge proof can be used to verify that a transaction is valid without revealing the details of the transaction.
The sole objective of the information on this website, which was gathered from external third-party sources, is general information. We make no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or completeness of our content. No information we provide should be taken as specific legal, financial, or other sorts of advice for you to rely on. Crypto is a very risky activity that can lead to significant losses; as a precaution, before making any decisions, please consult with your financial advisor. Nothing contained on our site constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, or endorsement.