OpenSea: Its Successes, Travails and The Rise of a Potent Competitor

NFTs are increasingly finding their ways into mainstream consciousness due to the mouthwatering prices they fetch and the possibility of actively participating in a fast-paced digital economy. At the center of this digital revolution are NFT marketplaces where the average NFT trader can mint, sell and buy NFTs.
The good thing about the NFT market is that there are several options to pick from. Therefore, it is safe to say that the landscape is highly competitive, which means that there is a high tendency that these marketplaces are going to try as much as possible to deliver innovative solutions. Due to these platforms’ penchant for innovation, the space can be said to be growing at a breakneck speed.
One of the platforms that have championed this movement is OpenSea, a blockchain-based marketplace that offers almost unlimited access to the NFT market. This website was one of the first movers in this space and it has retained its position as the largest marketplace for the last three years or so. However, now more than ever, OpenSea is facing stiff competition from other marketplaces, particularly Looksrare, which has incorporated a reward-powered system targeted at OpenSea’s existing users.
And so, there is a reason for new NFT users to explore more options as opposed to basing their decisions on the past successes of marketplaces. To this end, we have created a guide that highlights OpenSea, which is arguably the hottest NFT marketplace currently. Here, we will highlight its core features and how it has managed to become a juggernaut in the NFT industry. Also, we will discuss the latest threats to its success, including its flaws and the rise of a genuine competitor.
But first, let us walk you through some of the intricacies of NFT.
What are NFTs?

What are NFTs
Over the years, cryptocurrencies have become one of the most sought-after assets. Bitcoin, in particular, has emerged as an appealing alternative investment option with institutional investors increasingly adopting the digital asset in their portfolio. While the investment side of Bitcoin’s application has been put under the spotlight recently, it was its payment system that had originally fueled the cryptocurrency’s first attempt at mainstream success. Before all the hype about bitcoin’s potential investment capabilities, users paid more attention to the payment infrastructure of its network and the effectiveness of bitcoin as an alternative to fiat currency or traditional money. Notably, the whole narrative revolves around the capacity of bitcoin to exhibit elements of fungibility especially when it comes to exchangeability.
For an asset to qualify as a legal tender it must be exchangeable. In other words, one unit of the asset must be equal to another unit, the same way a dollar bill is always equal to another $1 bill. Similarly, 1 BTC will always be equal to another 1 BTC. This is the effect of fungibility and the reason bitcoin is an ideal alternative to fiat.
In contrast, non-fungibility connotes the uniqueness absent in assets like fiat, bitcoin, and ethereum. Non-fungible assets come with unique traits. Bearing this in mind, we can define non-fungible tokens (NFTs) as digital assets that establish rareness and uniqueness such that it is possible to differentiate between two or more assets existing in digital form and on the blockchain.
In addition to this, it allows us to implement rarity in the digital space. Most especially, this is important for developers or individuals looking to create collectibles or other items with some degree of rareness. As such, NFTs propel the valuation of digital items because it assures buyers that they are one of a kind or part of a limited collection.
It is worth mentioning that all these are made possible by blockchain implementations that allow us to store the metadata of each NFT token on an immutable and verifiable ledger. With this, anyone can confirm the authenticity of NFTs and even identify the owners. In other words, NFTs facilitate means to establish the ownership of digital assets while at the same time preserving their uniqueness.
When ownership is established, it becomes easier to sell the items in question in exchange for fiat or digital currencies. Therefore, NFT implementations aid the transfer and ownership of digital assets which at the moment is the whole essence of the emerging NFT market.
All in all, we can say that NFTs enable a new and improved way of creating, handling, authenticating, buying, and selling digital assets. Speaking of buying and selling digital assets, there are platforms specially designed to facilitate the trading of NFTs. These solutions are what we call NFT marketplaces.
However, before exploring the concept of NFT marketplaces, it is important to note that NFTs adhere to various token standards, depending on the blockchain where it was issued or created. For instance, NFTs created on the Ethereum ecosystem comply with a token specification called ERC721. In contrast, those that exist on Binance Smart Chain utilize the BEP-721 protocol. The specifications help developers build applications that are compatible with all the NFTs existing on a particular blockchain. In essence, when a developer builds an app that is compatible with the ERC721 protocol, chances are that the app will support most (if not all) of the NFTs issued on the Ethereum blockchain. It is this same system that determines the type of cryptocurrencies a crypto wallet supports.
Now that you understand some of the basics of NFTs, it is time to take a look at the importance of NFT marketplaces.
The importance of NFT marketplaces

NFT marketplaces are to the NFT market what crypto exchanges are to the crypto market. In other words, some gateways allow the average participant to access the NFT market seamlessly. In most cases, they simplify the processes involved in accessing, buying, and selling NFTs such that you and I do not require coding skills to navigate the NFT space. So, what an NFT marketplace does basically is that it provides all of the tools required to initiate NFT trades.
Note several functionalities determine how seamless it is to execute NFT trades, which is why it is advisable to research the workings of an NFT marketplace thoroughly before going ahead to register an account on it.
Bearing this in mind, we have created a comprehensive guide on how to choose a top NFT marketplace and some of the options you should consider. In this article, however, we have gone a step further to focus on arguably the most popular of the bunch, which is OpenSea. Here, we will take a look at the operations of OpenSea, identify its strongest suits, and even put the spotlight on its flaws. To get us started, let us first explore the workings of OpenSea.
What is OpenSea?

The introduction of the ERC721 token standard in 2017 marked a turning point in the NFT movement as projects began to introduce platforms that solely relied on the functionalities that NFTs provide. For instance, CryptoKitties became a crowd’s favorite because it capitalized on the possibilities that NFT offers by creating digital cats that can be owned, bred, and traded.
The explosion of this game kicked off the first phase of NFT growth and inspired the founders of OpenSea, Devin Finzer and Alex Atallah, to create a platform where the trading of NFTs like CryptoKitties can occur. Note that CryptoKitties has its native marketplace. Therefore, it was a bold move by OpenSea to develop a direct competitor with the hopes of attracting CyptoKitties’ users. One thing that the team behind OpenSea counted on was the apparent affordability of its infrastructure as it only charges a 2.5% commission on all sales finalized on its platform.
This was lower than what other marketplaces were charging. And so, it was only a matter of time before OpenSea became the go-to platform for those looking to sell their digital cats in exchange for ether. In addition to this, OpenSea had managed to simplify its features such that anyone could mint NFTs without having to master coding skills.
However, the NFT movement took a different turn when CryptoKitties and other NFT platforms at the time lost their appeal. During this era, the NFT craze took a nosedive with many arguing that the technology itself is yet to evolve and inspire more relatable applications. Regardless of the slump experienced during this period, NFT gradually became popular with digital artists who saw it as an avenue to monetize their artworks without involving middlemen-based services. With NFTs, the average artist can put his or her creation up for sale on a marketplace like OpenSea and automatically become visible to a growing network of NFT art lovers. More importantly, he gets to bypass intermediaries and keep most of the profits generated from the sales.
As such, OpenSea quickly evolved from an in-game asset-dominated platform to an ecosystem where independent artists can participate in a booming digital art market. At the same time, digital collectibles also began to spark a lot of excitement due to the absurd prices that NFTs like CryptoPunks were fetching in the secondary market. In essence, OpenSea has become an inclusive NFT marketplace where digital items of all kinds can be bought or sold. As such, whether you are looking to purchase in-game assets, collectibles, digital arts, music, or videos, chances are that you will find it listed on OpenSea. Today, it is considered the largest marketplace in the NFT sector with $5 billion worth of trading volume processed in January 2022 alone. At the time of writing this article, this was the record trading volume processed in a single month by OpenSea.
What are the features of OpenSea?
It may interest you to know that OpenSea has built a formidable presence in the NFT landscape over time. This is why the platform continues to attract NFT traders in their number. Although part of OpenSea’s successes can be attributed to its reputation and the first-mover advantage, we can also assert that the platform’s features have also made it the preferred destination for both NFT developers and NFT proponents alike. And so, you may be wondering: what are these features?
Simple interface and tools
One of the good things about OpenSea is that the platform has opted for less bogus tools and design such that users can start enjoying the world of NFTs with a click of a few buttons. It is worth mentioning that there is no need to write a single line of code to either mint NTTs or list them on the marketplace.
Unrestricted access to the minting tool
Unlike some of the NFT marketplaces found today, OpenSea does not implement any restrictions for its minting services. Anyone can take advantage of this tool to create content.
On-chain NFT trades
OpenSea conducts all of its operations on the blockchain. In other words, all sales are instantly executed and recorded on the blockchain. What this does is that it ensures that users access a peer-to-peer system devoid of intermediate services. This not only makes it cheaper to buy or sell NFTs but also ensures that the trade history is tamperproof.
It supports multiple chains
To expand its operations and offer more flexible solutions, OpenSea now supports three blockchains including Ethereum, Klaytn, and Polygon. As such, you can buy NFTs that exist on any of these three blockchains. Ethereum and Polygon, in particular, are two of the most critical blockchain networks for different reasons. On one hand, Ethereum houses a vast economy of blockchain apps and users. On the other hand, Polygon tries to eliminate Ethereum’s deficiencies by making it cheaper to interact with Ethereum-based applications and transact the hub’s growing list of tokens.
Gasless minting
One of the strengths of OpenSea is that it allows users to mint NFTs without having to pay transaction fees. This is a big deal because it provides a cheaper alternative to the often expensive minting process of the Ethereum blockchain.
You can find more information on how to get started with OpenSea, including the steps required to buy and sell NFTs, here.
What are the downsides of OpenSea?
Notably, it has not been smooth sailing for OpenSea as there have been numerous complaints about the performance of the website and the team’s approach to user experience and community building. More often than not, OpenSea has experienced technical issues that have caused the platform to be inaccessible to users. In one particular incident, users could not view their NFTs on Twitter or their wallets because OpenSea’s database went offline. The severity of this incident highlighted the negative impact of the unchecked influence that OpenSea had on the NFT market as a whole.
Also, the platform’s approach to community building has come under scrutiny. You see, blockchain apps often run a decentralized economy and governance system such that users become the major stakeholder and decision-makers. This is done by distributing a special token to allocate voting rights to users. More importantly, the platform’s revenue is collectively owned by the community who then decide the type of projects they want to invest in or the development research they are willing to pursue.
While this is the norm for apps that carry out all of their operations on-chain, OpenSea has opted for a more centralized governance system that has the team making all of the decisions without the system in place to carry the community along. Unlike most decentralized applications, the team behind OpenSea has full control over the revenue generated from the 2.5% commission charged on each trade executed on the platform. The platform does not have a native token designed to distribute voting power to users or reward them for their active participation. Even more surprising was the move to appoint a CTO with the plans of going public soon. It goes without saying that this goes against everything a decentralized application should stand for.
In addition to this, the company came under unwanted pressure when it was discovered a prominent member of the team was guilty of insider trading. The executive capitalized on non-public information to increase the chances of profiting off NFT trades.
Understandably, some experts explained that this incident further strengthens the argument that NFTs are as speculative as cryptocurrencies. Some have gone even further to argue that the insider trading scandal reinforces the need for regulators to explore how to best protect NFT traders. For instance, Will Gottsegen, in an opinion piece on Coindesk noted that NFT companies would eventually have to embrace regulatory oversights if the plan is to continue to attract and provide services to the mainstream audience: He Wrote:
“Crypto purists may bristle at the idea, but the path to establishing more trust in the market may involve ceding some ground to regulators. Say Instagram suddenly turned “likes” into NFTs and the first “like” on an iconic image came with the promise of monetary value down the line. It’s not hard to see how company employees could abuse inside information to get in early on, say, the first post from a celebrity new to the platform. How would it look for companies to fight this on their own? Would it involve dedicated enforcement teams and periodic surveillance of employee wallets? The crypto industry has a notoriously antagonistic relationship with regulation, but if NFTs are going to take off in a more mainstream way, buyers need to know they’ve got a fair shot. To help build that trust, oversight may be a price companies are willing to pay.”

While this debate was ongoing, OpenSea was also under fire for implementing restrictions on its shared storefront such that creators and developers can only mint a limited number of NFTs. According to the team, this decision was reached to reduce the occurrence of plagiarism which has been identified as one of the banes of the platform. However, not long after it implemented this restriction, OpenSea was forced to reverse its decision after the community pushed back. While explaining its actions via a tweet, the team stated that it had discovered that over 80% of the NFTs minted on its platform were either spam or plagiarized:
“Every decision we make, we make with our creators in mind. We originally built our shared storefront contract to make it easy for creators to onboard into the space. However, we’ve recently seen misuse of this feature increase exponentially. Over 80% of the items created with this tool were plagiarized works, fake collections and spam. We didn’t make this decision lightly. We made the change to address feedback we were receiving from our entire community. However, we should have previewed this with you before rolling it out. In addition to reversing the decision, we’re working through a number of solutions to ensure we support our creators while deterring bad actors. We commit to previewing these changes with you in advance of rolling them out. Please give us feedback along the way.”
Speaking of plagiarism, it is looking ever more likely that OpenSea will become the subject of lawsuits since it has become a breeding ground for counterfeit digital items and unlicensed artworks. Jeff Gluck, CEO of CXIP Labs, while confirming that OpenSea is at risk of facing a barrage of lawsuits, explained that these litigations will help in the formation of industry standards in terms of copyright protection. He stated:
“There are dozens of artists preparing lawsuits against OpenSea for selling infringing NFTs. These examples are a sneak preview of a wave of litigation heading towards the space. It’s both good and bad in that it discourages creativity and growth in some ways, but it’s beneficial because it will ultimately help provide some guidelines in terms of clear legal parameters and guidelines for the space.”
Marie Tatibouet, chief marketing officer of cryptocurrency exchange Gate.io, added that the apparent simplicity of minting techniques has made it a lot difficult to curb plagiarism in the NFT industry:
“Considering many platforms have made minting NFTs quick and easy, it’s also made it possible for those with malicious intent to produce and sell NFTs of copyrighted items. Platforms are slowly starting to adapt to this; however, it may remain to be an issue for the foreseeable future.”
Another contentious issue emerged when a defect in OpenSea’s system allowed users to buy NFTs way below the amount they are worth. While responding to this incident, OpenSea revealed that it was not fully responsible for this incident. Instead, the team blamed it on an existential downside inherited from the blockchain itself. The team wrote:
“This issue has been discussed as an “exploit” or a “bug,” but the reality is that it’s a fundamental feature of blockchain marketplaces: only the person who lists an item for sale can cancel that listing (i.e. OpenSea cannot cancel a listing on behalf of any user). This is, in many instances, a very good thing and an important aspect of what makes web3 special: your NFTs are completely in your control. There is a shared responsibility in the NFT community to educate newcomers to the benefits — and unique pitfalls — that come with interacting with blockchains. But as early members of the NFT space, we have a disproportionate share of that responsibility, and hold our product to a higher standard than most. We wish we had been clearer and more proactive in educating users on the risks of leaving orders uncancelled before transferring an NFT.”
In the aftermath of this conundrum. Gottsegen surmised that OpenSea’s struggles and its underwhelming response to crises show that the company tends to shy away from its responsibilities. He wrote:
“The NFT space has always been rife with plagiarism and spam, and OpenSea has played a major role in unleashing these forces. It’s difficult to imagine that a cap on the Shared Storefront would somehow stem the tide – but it’s OpenSea’s sorry reaction, more than anything else, that should have users worried. OpenSea and its investors don’t need to care about plagiarism because it actively helps their business model: the company takes a cut of each sale, and a sale’s a sale, legitimate or not. Venture capitalists and entrepreneurs have worked to make “creators,” not traders, the face of the NFT movement. Ultimately, it’s creators’ work on the line. Blaming users for plagiarism and blaming “the nature of the blockchain” for the uncanceled listings debacle, while saying nothing of poor communications and user experience (UX) design (there was no quick way to see uncanceled listings before this week), is a cheap way of avoiding responsibility.”
The rise of Looksrare?
Like OpenSea, Looksrare looks to anchor the NFT market by providing the infrastructure required to buy, sell and mint NFTs. In simpler terms, Looksrare is an NFT marketplace like OpenSea. However, it only came online in 2022, which makes it less experienced and reputable. But in that time, it has recorded trading volumes that rival that of OpenSea. 24 hours after it launched, the platform had already processed over $100 million worth of trades. While there are factors that helped Looksrare achieve this feat, the fact still remains that it has quickly risen in the ranks and may already be eyeing OpenSea’s position at the top echelon of the NFT market.
It is worth mentioning that Looksrare’s operation has been strategic from the very beginning. The creators had one thing in mind: create a business strategy that would compel OpenSea’s users to opt for its solutions. More specifically, it has implemented a more community-focused solution that revolves around an incentive-based economy. Knowing fully well that OpenSea has not issued a native token or attempted to reward its users, the creators of Looksrare have devised a means of offering a somewhat similar service, albeit with the incentives demanded by crypto proponents. In what is now called a vampire attack, Looksrare targeted the industry leader and enabled a superior incentive system with the hopes of cornering some of the established platform’s market share.
In particular, Looksrare launched the LOOKS tokens as the rewards for contributing to its ecosystem. More importantly, it identified OpenSea users that had processed at least 3 ETH worth of NFT trades in the last 6 months and offered them an opportunity of earning LOOKS tokens. The only caveat was that they have to list an item on Looksrare to become eligible for this reward.
In addition to this, Looksrare opted to charge a 2% commission as opposed to the 2.5% charged by OpenSea. Interestingly enough, the entirety of the revenue generated is allocated to those who opt to stake their LOOKS tokens. And so, we can say that Looksrare is looking to run a well-oiled incentive system that would ensure that users keep coming back for more.
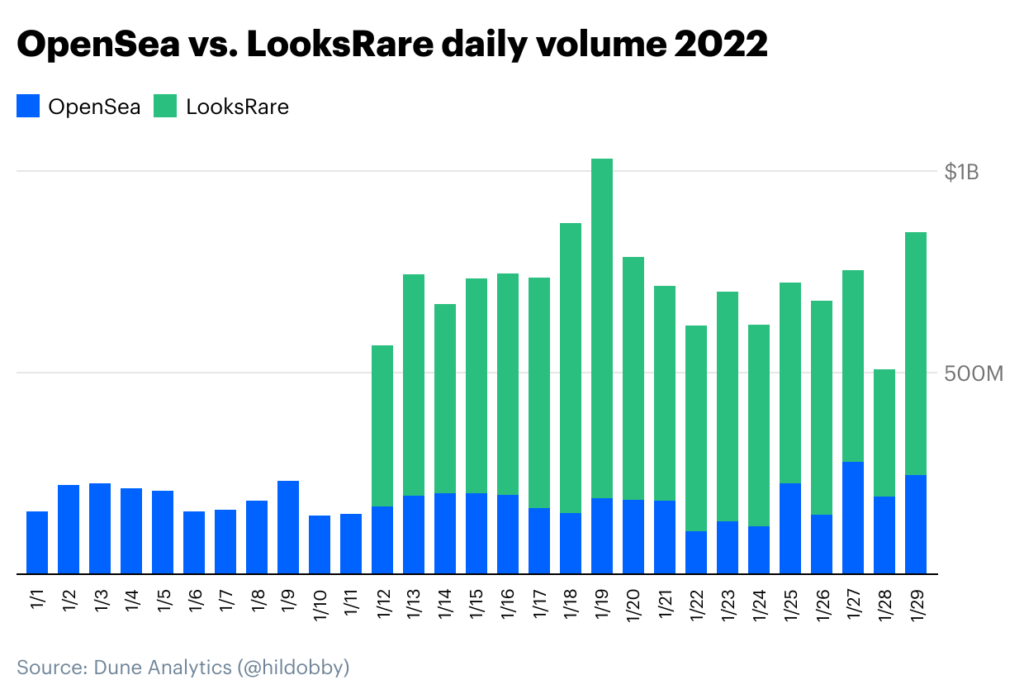
According to a report by Coinbase, Looksrare, thanks to its vampire attack on OpenSea, was able to achieve a $1 billion market cap in just 10 days after it launched and$9 billion by the end of January. The report reads:
“Due to the open-sourced nature of blockchains, the LooksRare team was able to identify OpenSea users who had traded at least 3 ETH worth of NFTs over the prior six months and airdrop them LOOKS tokens. However to claim these free tokens, users first had to list an NFT on the LooksRare exchange. Airdropping tokens to an existing community of active NFT traders proved effective, as NFTs flooded onto the new marketplace. The LOOKS token would climb to nearly $7 just 10 days after launch, fetching a $1B market cap in the process.”
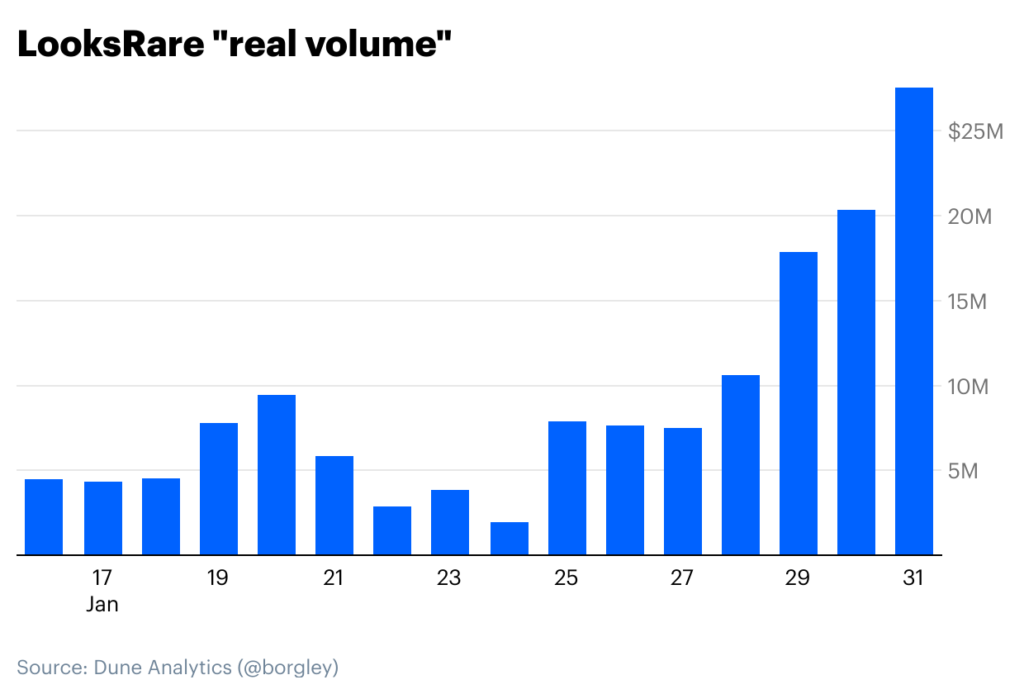
LooksRare volume
However, after taking a closer look at the data, there seem to be some anomalies that proved that Looksrare’s successes in terms of trading volume may not be as impressive as they initially appeared to be:
“The trading incentives is where things start to get interesting. It’s pretty simple: buy or sell an NFT on LooksRare and earn LOOKS. Rewards are paid out daily, based on the % of that day’s volume. Currently 2.8M LOOKS, or just under $10M USD at current prices, are being awarded daily. So far, a free airdrop was enough to get people to the platform, and a $10M daily reward has been enough to keep daily trading volumes outpacing OpenSea. However, when you look the total daily # of users, it’s clear that these volumes aren’t as impressive as they initially appear.”
It became clear that Looksrare’s trading volume did not correlate with the daily active users’ data. While it had recorded almost double of OpenSea’s daily trading volume, OpenSea still had way more active users than Looksrare. Notably, OpenSea had 20 to 40 times more active users. As such, it is safe to say that the impressive trading volumes recorded by Looksrare were indeed fueled by a handful of traders trying to initiate activities with the sole aim of earning incentives. According to the report published on Coinbase’s blog, this indicated that traders were engaging in activities that could be classified as wash trading:
“There’s nothing stopping a user from swapping the same NFT back and forth between their own wallets at a high dollar amount. Since daily rewards are paid out as a % of the day’s volume, if, for example, someone can wash trade their way to 10% of that day’s volume, they can net $1 million in LOOKS. The wrinkle here is that for every trade, users must pay a 2% fee priced in ETH. The math works out such that the fees traders are paying in ETH are roughly equal to the rewards being paid in LOOKS. As such, traders are basically swapping ETH for LOOKS, which will pay off should the price of LOOKS appreciate relative to the price of ETH. Essentially, there’s an interesting bit of game theory in motion, as early adopters will be rewarded should the LooksRare platform succeed.”
However, after carefully analyzing the activities on Looksrare, it was clear that not all trades executed on this platform were illegitimate. According to Crypto Slam, around $1 billion of the $9 billion volume recorded in January 2022 was not associated with wash trading. To put this into perspective, this was more than the volume processed by NFT marketplaces like Rarible, SuperRare, and Foundation for the entirety of 2021.
At this juncture, the question is: What are the chances that Looksrare will overtake OpenSea, knowing fully well that its incentive system would not always be as attractive as it is presently?
Although it is impossible to know for sure, we can use the outcome of other vampire attacks as references. For example, Sushiswap is yet to dethrone Uniswap, even though it managed to steal a chunk of Uniswap’s market share. The same is true for other solutions that forked from existing projects. As such, if previous events are anything to go by, the chances that Looksrare will usurp OpenSea is slim:
“We can look to its vampire attacking predecessor, SushiSwap, for a glimpse into what the future may hold. SushiSwap by many measures has remained relevant after its initial rewards dried up. They continued to innovate and deploy across multiple chains, with nearly $5B in TVL today. However, usurp Uniswap they did not. Uniswap eventually launched a token of its own (there’s speculation that OpenSea may one day do the same) and has maintained its standing as crypto’s dominant DEX with over $7.5B in TVL today. It’s also worth noting that no contentious hard fork (Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum Classic, etc) or vampire attacker (SushiSwap, Swerve, etc) has ever supplanted an incumbent.”
