How to Pick the Best Wallet for Storing Cryptocurrencies?

Choosing a wallet for securing cryptocurrencies can be one of the most complicated parts to the process of investing in cryptocurrencies. It is tempting to just leave the funds on an exchange. Leaving funds on an exchange adds unnecessary risks. Users both give up the control of the funds to the exchange and expose themselves to the business risks of the exchange. If the exchange is hacked or goes out of business, a users funds will likely be lost.
We simplify the process of choosing a wallet here. We present the key considerations you need to take into account when picking a wallet. While the intricacies of wallets can go really deep, the following considerations will provide users with a strong base layer of security to store their cryptocurrencies.
Where is the private key stored?
The public and private key are concepts which cause much confusion in cryptocurrencies. A good analogy for understanding the public and the private key is to think of it in terms of your email address. You share your email address with colleagues or friends so that they can communicate with you. You never share your password to your email account with them as this would enable them to access sensitive information. The private and public key operates in the same way. The public key enables other accounts to send funds to you. The private key would enable them to access and steal your funds.
For that reason, how the private key is stored for a wallet is the single most important consideration when choosing a wallet. If the private key is stored by a third party and they can access it, this means that they have access to the wallet owners funds. Wallets that are operated by exchanges or that are based in the web browser are typically the poorest forms of security due to the private key mostly being controlled by the third party providing the wallet. Other types of wallets such as hardware wallets, paper wallets, and desktop wallets mostly put the user in complete control of their private key.
Are the funds kept in cold storage or hot storage?
Another commonly heard reference in wallet terminology is whether the funds are held in cold storage or hot storage. This simply refers to whether the funds are connected to the internet or not. Funds held in cold storage are in a wallet which is disconnected from the internet. This is a more secure method of storing funds. Hot storage is more convenient as users can easily monitor the balance of the wallet and send transactions.
What are the different options?
Once you are familiar with hot storage and cold storage along with private and public key, you are left with a number of key options to choose from when picking a wallet. The main wallet types are the following:
Hardware Wallets
- Security 5/5
- Functionality 5/5
- Ease of Use ⅘
- Convenience 3/5
Hardware wallets represent the gold standard in security. Hardware wallets are typically devices similar to a USB. The private key is stored on the device itself so that the funds on the wallet are secure even if they are used on a compromised computer.
Hardware wallets leverage the benefits of both cold and hot storage. Funds are stored offline when the wallet is disconnected and users can connect the wallet to a computer to manage their account or send transactions.
The only real downside is that users have to pay to obtain a hardware wallet. They are worth the investment if users hold a significant amount of cryptocurrencies. It may be a price to pay but it provides a greater level of security to the user’s funds. The main hardware wallets are Trezor by SatoshiLabs, Ledger Nano S by Ledger, and KeepKey.

Desktop
- Security ⅘
- Functionality 5/5
- Ease of use ⅘
- Convenience ⅗
Desktop wallets come in a wide variety of formats. They typically store the private keys for the wallet on the users hard drive so that they are the only ones that can access them. It is important when using a desktop wallet to know exactly how the private keys are going to be stored.
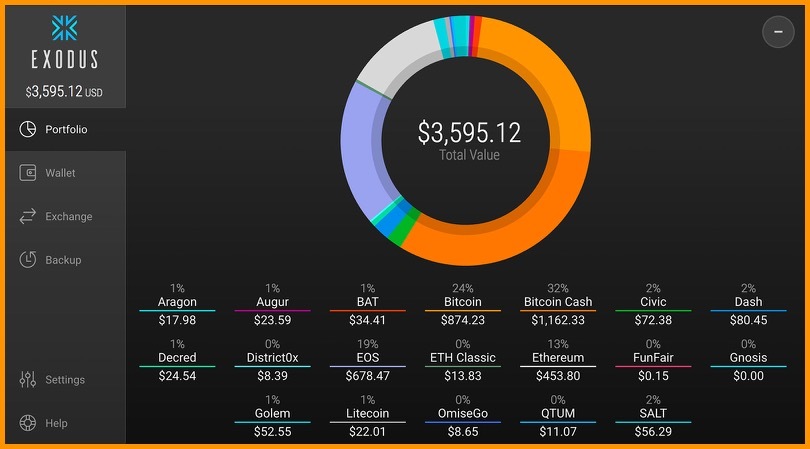
The wallets vary in their features, functionality, and support. One of the most popular desktop wallets is Exodus which supports almost 100 cryptocurrencies and provides features to assist users in managing their portfolio.
Mobile Wallets
- Security ⅗
- Functionality 5/5
- Ease of use ⅘
- Convenience 5/5
Mobile wallets also come in a wide variety. They typically store the private key on the user’s device and encrypt it. It is important for users to be aware of how mobile wallets store the private key. Private keys stored on the wallet providers servers are highly insecure.
Mobile wallets rank highly in terms of convenience. They enable users to easily receive and send payments as they go about their day-to-day activities. A QR code can be generated so that others can easily scan it to send payments. Users can easily pay merchants that accept cryptocurrency via their mobile wallet. Wallets such as Coinbase Wallet, formerly called Toshi, also enable users to interact with decentralized applications (DApps) on the Ethereum blockchain.
Web-Based Wallets
- Security ⅖
- Functionality ⅘
- Ease of use ⅘
- Convenience ⅘
Web-based are wallets accessible on the web browser. The private key for these wallets is typically stored on the wallet providers server making them insecure. Some of these wallets provide good services in terms of functionality such as blockchain.com. The only wallets which should be considered in this category are the ones which apply high levels of encryption to the private key so that it is likely not accessible to anyone but the wallet user.
Exchange-Based Wallets
- Security ⅕
- Functionality ⅗
- Ease of use 5/5
- Convenience 5/5
Exchange-based wallets are the poorest level of security in terms of wallets. Using an exchange based wallets exposes the user to all the business risk of the exchange that operates the wallet. Funds of the exchange users are typically pooled together as well so if a hack occurs, all of the funds are at risk.
Paper-Based Wallets
- Security 5/5
- Functionality ⅖
- Ease of use ⅕
- Convenience ⅕
Paper-based wallets are a valid option for those who are comfortable with how wallets work. Paper wallets provide a public and private key on paper. Sending money to the wallet keeps them entirely in cold storage. If a user needs to complete a transaction, they can import the wallet into a wallet provider which supports paper wallets such as blockchain.com

